Hernia Surgery

Overview of Hernia Surgery
A hernia is a pathological condition characterized by the protrusion of an organ or tissue through a weakened area in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. This defect commonly manifests in regions such as the abdominal wall or the groin, where the integrity of the muscular or fascial barrier is compromised. The result is the abnormal displacement of internal structures, which can lead to a range of clinical symptoms, including pain, discomfort, or even life-threatening complications in more severe cases.
Hernia repair surgery is a definitive intervention aimed at correcting this anatomical defect. The objective of surgical treatment is to restore the normal anatomical alignment by repositioning the herniated tissue or organ and reinforcing the weakened area of the muscle or connective tissue. The surgical approach is selected based on several factors, including the type of hernia, its location, the patient’s overall health, and the risk of complications.
Various techniques can be employed for hernia repair, each with specific advantages and indications. Traditional open surgery involves a single, larger incision through which the hernia is accessed, and the defect is repaired, often with the use of synthetic mesh to provide additional strength to the area. Alternatively, minimally invasive methods, such as laparoscopic surgery, utilize smaller incisions and a camera to guide the repair process, resulting in reduced recovery times and a lower risk of complications. Robotic-assisted surgery further enhances the precision and flexibility of the procedure, providing the surgeon with advanced tools to perform the repair with greater accuracy and potentially improving patient outcomes.
Each of these surgical techniques has been refined over time to optimize patient recovery, minimize postoperative pain, and reduce the risk of recurrence, allowing for individualized treatment plans based on the specific needs of the patient.
Types of Hernia Surgery
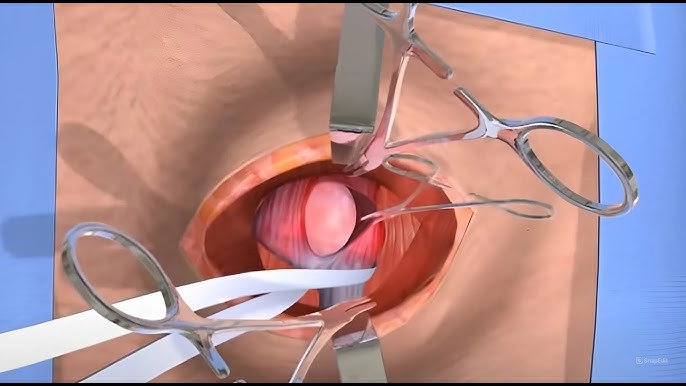
Open Hernia Repair (Herniorrhaphy/Hernioplasty)
A single large incision is made to push the herniated tissue back and reinforce the area with sutures or a mesh.

Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
Minimally invasive technique using small incisions and a laparoscope.
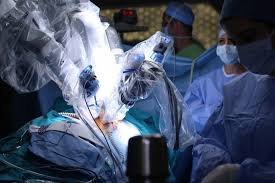
Robotic Hernia Repair
Similar to laparoscopic surgery but performed with robotic assistance for greater precision and flexibility.
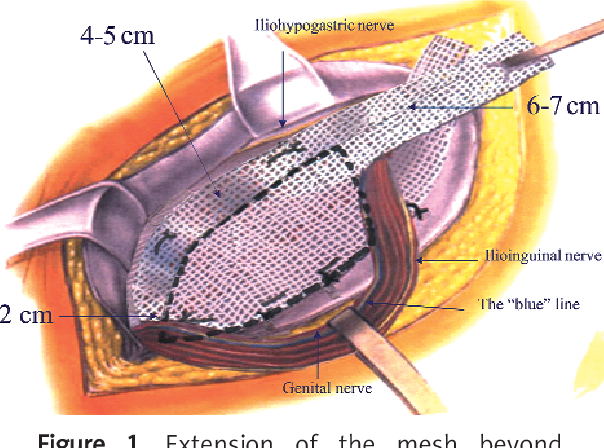
Tension-Free Mesh Repair
Involves placing a synthetic mesh over the weakened area to provide support.
Booking form
Advantages
Permanent Repair:
Surgery provides a long-term solution, reducing the risk of recurrence.
Minimally Invasive Options:
Laparoscopic and robotic techniques result in smaller incisions, less pain, and faster recovery.
Improved Strength:
Mesh reinforcement strengthens the affected area, preventing future hernias.
Reduced Pain:
Advanced techniques minimize post-operative discomfort.
Quick Recovery:
Many patients return to normal activities within a few weeks.
Outpatient Procedures:
Many hernia repairs are performed as day surgeries.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Curabitur laoreet cursus volutpat. Aliquam sit amet ligula et justo tincidunt laoreet non vitae lorem. Aliquam porttitor tellus enim, eget commodo augue porta ut. Maecenas lobortis ligula vel tellus sagittis ullamcorperv vestibulum pellentesque cursutu.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Curabitur laoreet cursus volutpat. Aliquam sit amet ligula et justo tincidunt laoreet non vitae lorem. Aliquam porttitor tellus enim, eget commodo augue porta ut. Maecenas lobortis ligula vel tellus sagittis ullamcorperv vestibulum pellentesque cursutu.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Curabitur laoreet cursus volutpat. Aliquam sit amet ligula et justo tincidunt laoreet non vitae lorem. Aliquam porttitor tellus enim, eget commodo augue porta ut. Maecenas lobortis ligula vel tellus sagittis ullamcorperv vestibulum pellentesque cursutu.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Curabitur laoreet cursus volutpat. Aliquam sit amet ligula et justo tincidunt laoreet non vitae lorem. Aliquam porttitor tellus enim, eget commodo augue porta ut. Maecenas lobortis ligula vel tellus sagittis ullamcorperv vestibulum pellentesque cursutu.
Why choose
Why People Choose Robotic Surgery
Hernia surgery is a safe and effective solution that improves both function and quality of life, offering a range of options tailored to patient needs and hernia complexity.
Symptom Relief:
Surgery alleviates pain, discomfort, and the risk of complications like strangulation.
Preventing Complications:
Untreated hernias can lead to serious issues, including bowel obstruction and tissue strangulation.
Enhanced Quality of Life:
Surgery restores mobility and comfort, allowing patients to resume daily activities.
Minimized Downtime:
Minimally invasive options ensure quicker recovery and return to work.
Improved Confidence:
Patients feel more secure knowing the hernia has been repaired effectively.
Long-Term Benefits:
Mesh repairs offer durable results with a low recurrence rate.
